A blood clot in the brain, medically termed cerebral thrombosis, is a medical emergency requiring prompt intervention. When a clot forms in a brain artery, it restricts blood flow to a specific region, depriving brain cells of vital oxygen and nutrients. This can cause permanent damage, leading to severe disabilities or even death. Recognizing the warning signs and acting swiftly are crucial for minimizing brain damage and ensuring the best possible outcome.
What is a blood clot in the brain?
A blood clot is a clump of cells that form in the bloodstream, usually to stop bleeding after an injury. However, a clot in the brain within a blood vessel can be detrimental. This clot can obstruct blood flow to part of the brain, leading to potentially serious consequences such as a stroke or other neurological complications.
Types of Blood Clots in Brain
There are two main types of blood clots that can occur in the brain.
These are:
Ischemic stroke
This is the most common type, arising when a clot blocks a blood vessel, interrupting blood flow to a part of the brain. Brain cells in the affected area are starved of oxygen, leading to tissue death.
Hemorrhagic stroke
This occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding within the brain. The accumulated blood puts pressure on surrounding brain tissue, damaging cells and disrupting normal function.
What causes blood clots in the brain?
Several factors can contribute to the formation of blood clots in the brain.
These include:
High blood pressure
Uncontrolled hypertension damages blood vessel walls, making them more prone to rupture or narrowing, which can lead to clot formation.
High cholesterol
Elevated cholesterol levels can cause fatty deposits to build up in arteries, narrowing the passage and increasing the risk of clots.
Certain medical conditions
Atrial fibrillation, a heart rhythm irregularity, can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the heart and traveling to the brain.
Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and thickens the blood, creating a favorable environment for clot formation.
Family history
Having a close relative with a history of stroke increases your own risk.
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Brain
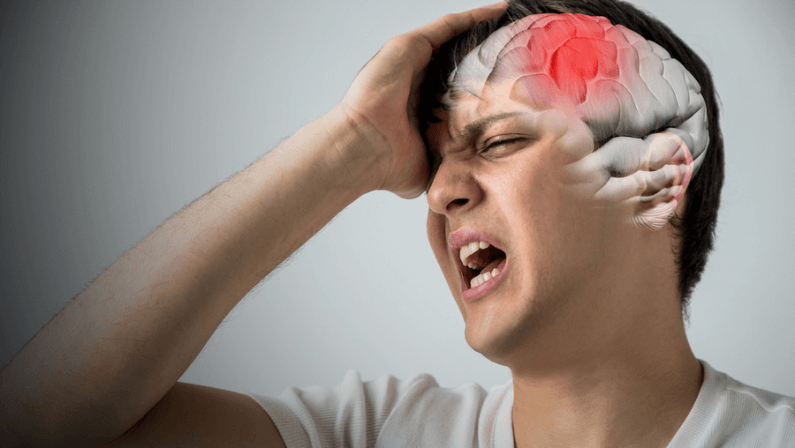

What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the head? What does a blood clot in brain feel like? A blood clot in the brain can manifest through a sudden onset of various symptoms. Recognizing these warning brain blood clot signs and seeking immediate medical attention is critical:
Blurry or darkened vision
Sudden changes in vision, like blurred or dimmed eyesight in one or both eyes, can indicate a clot affecting the visual areas of the brain.
Severe headaches
A sudden and intense headache, often described as the “worst headache of your life,” can be a warning sign of a stroke.
Slurred speech
Difficulty speaking clearly or forming words can occur if the brain region controlling speech is affected by a clot.
Numbness or weakness
Sudden numbness or weakness, typically on one side of the body (face, arm, or leg), is a common symptom of a stroke.
Acute paralysis
A sudden loss of movement or control over a limb or one side of the body can signify a major blood clot blocking a vital brain area.
Trouble walking
Difficulty walking, maintaining balance, or experiencing dizziness can also be indicative of a stroke.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in Brain
Rapid diagnosis is essential for timely treatment. Doctors will consider the patient’s symptoms and medical history, and conduct various tests, including:
- Brain imaging: CT scans or MRI scans can help visualize the brain and identify any signs of bleeding or damage caused by a clot.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help assess cholesterol levels and blood clotting time, and identify any underlying medical conditions that may have contributed to the clot formation.
Possible Risks and Complications Related to Blood Clot in Brain
Ignoring the signs of a blood clot in the brain can lead to devastating consequences. Potential risks and complications include:
- Permanent brain damage: Brain cells deprived of oxygen due to the clot can die, leading to lasting impairments in speech, movement, cognitive function, or memory.
- Seizures: Disruptions in brain activity caused by the clot can trigger seizures.
- Coma: In severe cases, a large clot can lead to extensive brain damage and coma.
- Death: If left untreated, a blood clot in the brain can be fatal.
How to Treat Blood Clots in Brain
What is the treatment of blood clots in brain? Recognizing the signs of a blood clot and seeking immediate medical attention at Aether Health, are crucial for successful treatment and minimizing potential brain damage. Here’s a breakdown of the treatment approaches:
Time-Sensitive Clot Removal
Acting quickly is vital. Doctors prioritize dissolving the clot as soon as possible to restore blood flow and limit tissue death. This can be achieved through:
- Thrombolytic therapy: Clot-busting medication is administered intravenously to dissolve the clot. This treatment is most effective within a specific time window, usually up to 4.5 hours after stroke onset.
Minimally Invasive Clot Removal
When medication isn’t suitable or fails to work, minimally invasive procedures may be employed:
- Thrombectomy: A thin catheter is inserted into an artery and navigated to the clot location in the brain. Using microscopic tools, the interventional radiologist retrieves the clot, restoring blood flow.
Surgical Intervention
In some cases, surgery might be necessary:
- Craniotomy: A surgical procedure to remove a large blood clot putting significant pressure on the brain or repair a weakened blood vessel prone to rupture and bleeding.
Supportive Care
Following the initial clot removal procedure, supportive care plays a vital role in the recovery process:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe blood thinners to prevent further clot formation and medications to manage conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol that elevate the risk of stroke.
- Rehabilitation: After a stroke, physical, occupational, and speech therapy play a crucial role in helping the individual regain lost motor skills, improve speech and cognitive function, and learn to cope with any lasting impairments.
The success rate of treatment and the extent of potential recovery largely depends on how quickly the blood clot is addressed. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to minimize brain damage and improve the chances of a full or near-full recovery.
Rehabilitation After Cerebral Blood Clot
Rehabilitation after a blood clot in the brain is a crucial aspect of the recovery process. It focuses on helping the individual regain lost abilities and functions affected by the stroke.
A comprehensive rehabilitation program may involve:
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist works with the individual to improve mobility, coordination, and balance. This can involve exercises to strengthen weakened muscles, relearn movement patterns, and regain independence in daily activities.
- Occupational therapy: An occupational therapist helps the individual relearn daily living skills that might have been affected by the stroke, such as dressing, bathing, and self-care.
- Speech therapy: A speech therapist helps individuals who experience difficulty speaking, understanding language, or swallowing after a stroke.
The rehabilitation journey can be challenging, but with dedication and a tailored therapy program, significant improvements can be achieved.
How to Prevent or Avoid Blood Clots in Brain

While certain risk factors cannot be controlled (age, family history), adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of blood clots:
1. Maintain a healthy weight.
Obesity is a contributing factor to high blood pressure and other conditions that elevate the risk of stroke.
2. Eat a balanced diet.
Limit intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Choose a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to promote heart health.
3. Exercise regularly.
Regular physical activity helps manage weight, lower blood pressure, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
4. Manage chronic conditions.
Effectively controlling conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes through medication and lifestyle modifications is crucial.
5. Stop smoking.
Smoking damages blood vessels and significantly increases the risk of blood clots.
6. Limit alcohol consumption.
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to stroke risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recognizing the seriousness of a blood clot in the brain, you likely have many questions. This section addresses some frequently asked concerns to shed light on the condition and empower you with crucial information.
Is it risky to have blood clots in the brain?
Yes, blood clots in the brain are highly dangerous and require immediate medical attention. They can cause permanent brain damage, disability, and even death.
Are brain clots curable?
Blood clots themselves can be dissolved or removed through medication or procedures. However, the brain damage caused by the clot might be permanent depending on the severity and the duration of blood flow blockage.
Can stress induce blood clots in the brain?
While chronic stress can contribute to factors like high blood pressure, which increases the overall risk of stroke, stress alone is not a direct cause of blood clots in the brain.
When should I seek emergency medical care?
If you experience any sudden onset of symptoms like severe headache, weakness, slurred speech, vision changes, numbness, or difficulty walking, call emergency services immediately. Early intervention is critical for minimizing brain damage and improving treatment outcomes.
Can a person die from a stroke?
Yes, a person can die from a stroke. A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, either by a clot blocking a blood vessel (ischemic stroke) or by a blood vessel bursting and causing bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). If blood flow is not restored promptly, brain cells begin to die, leading to potentially serious consequences, including death.
What kinds of questions do you need to ask your doctor?
Regarding questions to ask your doctor about stroke, here are some important ones:
- What type of stroke do I have (ischemic or hemorrhagic)?
- What caused my stroke, and what risk factors do I have for future strokes?
- What treatment options are available for my condition?
- What are the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option?
- How soon should treatment be initiated, and what is the optimal timeframe for recovery?
- What lifestyle changes can I make to reduce my risk of future strokes?
- Are there any medications I need to take, and how should I take them?
- What warning signs or symptoms should I be aware of that might indicate another stroke?
- When should I follow up with you or seek medical attention if I experience any concerning symptoms?
- Are there any support groups or resources available to help me cope with the effects of stroke and manage my recovery?
Taking Charge of Your Health: Early Action Saves Lives
Blood clots in the brain are time-sensitive emergencies. Acting swiftly upon recognizing the warning signs and seeking immediate medical attention is crucial for minimizing brain damage and ensuring the best possible outcome. Early diagnosis allows doctors to implement necessary treatment measures, such as clot removal or blood thinners, to restore blood flow and limit damage.
Residents have easy access to emergency medical care in Pearland, Texas at facilities like Aether Health, which provides 24/7 emergency services. Their team of medical professionals is equipped to handle time-sensitive situations and ensure patients receive the necessary care promptly. Contact them today!